Ethertoff
=========
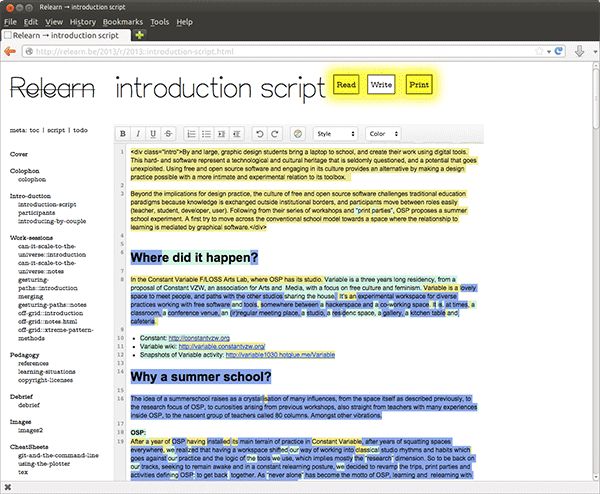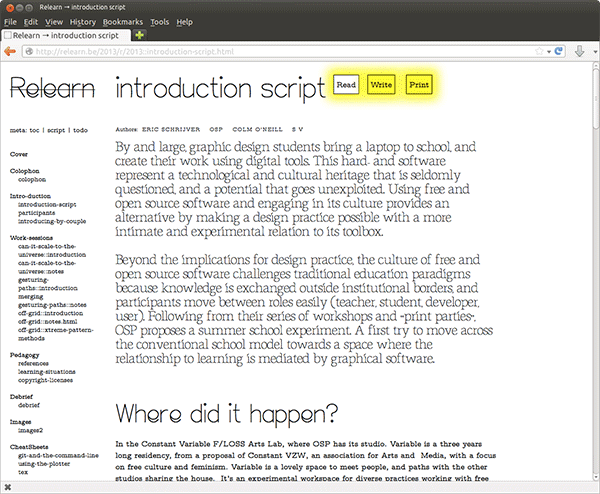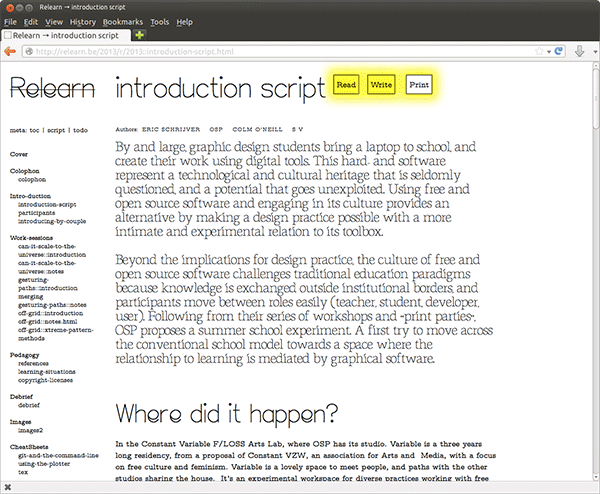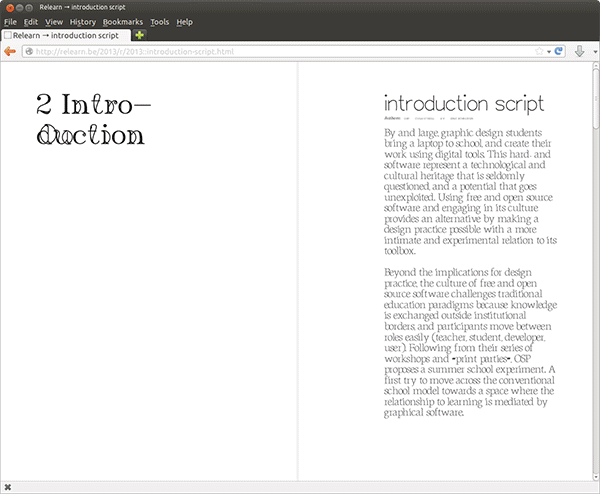
Ethertoff is a simple collaborative web platform, much resembling a wiki but featuring
realtime editing thanks to Etherpad. Its output is constructed with equal love for print
and web.
> Just a question: I thought it was ethertopff and not ethertoff but I don't
> remember why. What is the actual name?
>
> Well someone misspelled ethertopdf as ethertopf which sounds like römertopf
> and than somebody else understood ethertoff like chokotoff and chokotoff
> being Bruxellois I thought it might be the best of all these references
Ethertoff has been initially developed for the OSP 2013 Summerschool bearing the name ‘Relearn’.
Ethertoff is structured as a wiki where each page constitutes an Etherpad.
The pad is available to logged in users (‘write-mode’).
The text of the pad is available to everyone (‘read-mode’).
Ethertoff is a shell for an Etherpad installation hosted on the same domain.
This integration is based on Sofian Benaissa’s bridge between Django and Etherpad,
originally created for THINK WE MUST/CON-VOCATION a performance during Promiscuous
Infrastructures entrelacées, an exhibition by the collective Artivistic at SKOL.
-
-
-
- - -
## Installation instructions
Requires Django 2.0 and python 3, pip.
First create and install a virtual environment in the repository.
cd tools.ethertoff
sudo apt install virtualenv
virtualenv -p python3 venv
source venv/bin/activate
Then:
sudo aptitude install python-dev libxml2-dev libxslt-dev libz-dev
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install https://github.com/devjones/PyEtherpadLite/archive/master.zip
pip install https://github.com/aleray/markdown-figures/archive/master.zip
cd ethertoff
cp local_settings.py.example local_settings.py
# OPTIONAL: Change database details in local_settings.py
cd ..
python manage.py migrate
Change the info of your domain name and website name in the Sites section on
. **Do not add "http://" in your domain name,
otherwise the Re-index function won't work.**
### If you have the error "Site matching query does not exist"
Open the python shell
python manage.py shell
And then do the following (replace the "domain" and "name" with your own info):
from django.contrib.sites.models import Site
site = Site.objects.create(domain='example.com', name='example.com')
site.save()
## Install Etherpad-lite
mkdir -p ~/src
cd ~/src
git clone https://github.com/ether/etherpad-lite.git
## --> install node js
Install Make:
sudo aptitude install build-essentials
Linux Binaries (.tar.gz) from http://nodejs.org/download/
## Launch Etherpad-lite
run Etherpad with:
~/src/etherpad-lite/bin/run.sh
Your Etherpad is running at http://127.0.0.1:9001/
In Etherpad’s folder, you will find a file called APIKEY.txt
you need its contents later
## Launch Ethertoff
Run the server:
python manage.py runserver
visit the admin at: http://127.0.0.1:800/admin/
you can login with the superuser you created when you synced the database
Now, on the Django admin:
Etherpadlite > Servers > Add
# if local
url: http://127.0.0.1:9001/
# if on a server
url: http://domainname/ether/
api_key: the contents of the file APIKEY.txt in Etherpad files
Go back to the admin home, and then add a new group:
Auth > Groups > Add
Go back to the admin home, and then add the superuser (and all needed users) to the group you just created
Auth > Users
Go back to the admin home, and then create an Etherpad Group based upon the group and the server you just created.
Etherpadlite > Groups > Add
Now Ethertoff is served at http://127.0.0.1:8000/ locally, or on your domain name on a server.
You can set the site name, that appears on the header, in the ‘sites’ app in the admin.
# Extra challenge! Installing on a server.
Some extra challenges. Basically we can split it up like:
example.com / -> django
/ether/ -> etherpad
/static/ -> django static files
To test if everything is working, you can use screen to run gunicorn and Etherpad scripts at the same time, and then use a daemon like Supervisor to run them in the background.
## MYSQL
# pip install "distribute>0.6.24"
sudo aptitude install default-libmysqlclient-dev python-dev
pip install MySQL-python mysqlclient
## DJANGO
The django application runs through mod_wsgi (Apache) or gunicorn
(nginx), or whatever way you prefer to run your wsgi python apps.
You map it to the root of your domain.
For django, we need to set up some folder where the static files
are collected. You do this with the command: `python manage.py collectstatic`
This folder we then serve through nginx or apache, and map to the
folder /static/.
sudo aptitude install nginx
pip install gunicorn
cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
# (edit nginx config file)
sudo vim ethertoff.conf
cd ../sites-enabled/
sudo ln -s ../sites-available/ethertoff
cd ethertoff_directory/
# (edit gunicorn config file)
vim run.sh
chmod +x run.sh
sudo service nginx start
# Run the server
./run.sh
To run the server in the background, use Supervisor daemon.
## ETHERPAD
Etherpad, finally, runs as its own server. You probably need to use
a supervisor such as supervisord to make sure it keeps running.
You will also need to set up a database, because its default database
is not intended for use on servers. Finally, you will need to reverse
proxy the Etherpad process from your main web server, mapping it to
a folder such as /ether/.
## SUPERVISOR
To run django and etherpad in the background.
sudo aptitude install supervisor
# Edit specific config file for each application in /etc/supervisor/conf.d/
### Example of config file
[program:pads]
directory = /absolute/path/to/etherpad-lite/bin/
user = username
command = /absolute/path/to/etherpad-lite/bin/run.sh
stopwaitsecs=60
stdout_logfile = /absolute/path/to/etherpad-lite/logfile.log
stderr_logfile = /absolute/path/to/etherpad-lite/logfile.log
# Then run the apps daemon
supervisord
supervisorctl start app_name